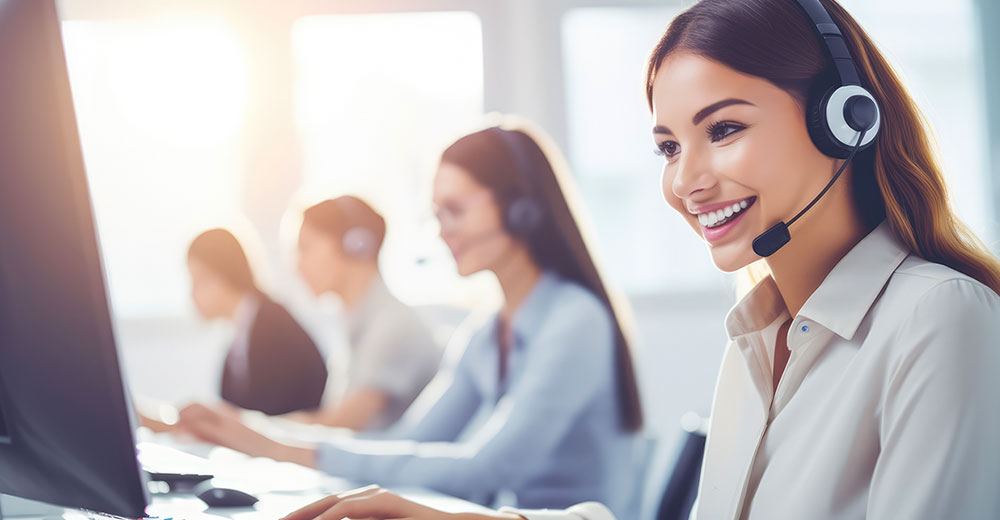
Artificial intelligence-powered bots used in customer service settings are finally learning to get along with human agents. Or is it the other way around?
Either way, the friction that existed as humans learned to divest some of their more routine service tasks is producing better efficiency at smoothing out CRM encounters, according to Michael Bradford, head of operations, Americas, at HappyOrNot — a provider of customer feedback and analytics tools designed to capture real-time, actionable insights to improve customer satisfaction and business operations.
The battle between bots and humans raged for years in customer service. Now, it seems that many American workers are embracing the benefits of AI.
Recent research by integration platform as a service (iPaaS) provider SnapLogic reveals that 68% of employees want their companies to introduce more AI technologies. Meanwhile, studies from human capital and workforce management solutions provider UKG indicate that 56% of employees already use AI on a daily basis.
CMSWire reports that 60% of customer experience (CX) leaders expect AI to transform or significantly impact addressing obstacles with existing CX operations. Additionally, according to digital consulting firm Deloitte, 81% of contact center execs are investing in agent-enabling AI.
“American workers are increasingly welcoming AI, not out of fear of replacement but because they see its potential to augment their capabilities,” Bradford told CRM Buyer.
He noted that the repetitive, data-heavy tasks that AI excels at are often the most tedious aspects of a job.
Driving Factors for AI Adoption in Customer Service
By automating these tasks, AI frees human workers to focus on higher-order skills like critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence. In these job areas, humans remain irreplaceable.
Additionally, AI can provide real-time data and insights that empower workers to make better decisions. These capabilities, in turn, ultimately lead to a more fulfilling and productive work experience.
HappyOrNot’s sentiment analysis tools are a striking example of why AI-powered CRM is on a growth spree. Generative AI in CRM applications empowers workers by automating mundane tasks like summarizing customer interactions or generating personalized responses.
This automation frees up time for agents to engage in complex conversations that require empathy and understanding. Bradford noted that generative AI ensures faster response times and a more consistent customer experience. “Ultimately, it is a win-win scenario for workers and customers,” he said.
Research Highlights Impact of AI on Customer Success
Recent studies indicate that more than half (56%) of business owners now use AI for customer service tasks. Bradford suggests that this number is likely to rise through continuing feature adoption. Businesses recognize AI’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness for tasks like routing inquiries, providing basic troubleshooting steps, and answering FAQs.
Bradford explained that HappyOrNot’s real-time feedback platform integrates seamlessly with AI chatbots, allowing businesses to identify customer pain points and escalate complex issues to human agents where needed.
However, for greater success in this regard, effective AI integration requires a managerial shift from control to collaboration. He cautioned that managers must focus on creating workflows where human and AI strengths complement each other.
“This requires ongoing training and development to ensure agents can work seamlessly with AI tools,” said Bradford.
For instance, AI handles rote tasks, while human agents leverage their emotional intelligence, communication skills, and problem-solving abilities to tackle complex customer issues.
Global Trends in Training Humans on AI
According to Bradford, the trend of AI bots and humans working together in customer service is not just an American phenomenon. Businesses worldwide are recognizing the benefits of this collaborative approach. His company’s global reach shows this trend unfolding across diverse markets.
Companies are using AI bots and features in various ways based on use cases integrated within the firm’s platform. For example, AI streamlines the initial contact process, routing inquiries to the most appropriate agent based on keywords or sentiment analysis.
AI chatbots handle basic questions and provide 24/7 support, freeing up human agents for more complex issues. Real-time feedback analysis tools integrate with AI to analyze customer sentiment and identify areas for improvement.
“The level of training needed for human employees when implementing AI in customer service varies,” Bradford explained.
For essential platforms, training might focus on understanding how the AI tool works and best practices for collaborating with it. More sophisticated AI may require more profound training in data analysis and interpretation.
Job Threats Minimal in AI-Human Working Relationship
“AI is not about phasing out human agents but empowering them,” insisted Bradford.
AI allows agents to focus on building relationships with customers and resolving complex issues. These benefits, in turn, lead to higher customer satisfaction and improved agent morale, he added.
His company found that redesigning the virtual and hybrid workplace with humans at the center is crucial for success. It improves an organization’s worker experience and delivers actual business results.
However, companies need to approach the adoption of AI technology with a clear plan to improve customer services. This strategy could involve providing CX human agents with the resources and training to excel in a human-AI collaborative environment.
“When human well-being is prioritized, it leads to more positive work experience,” counseled Bradford. “This translates into better customer service and, ultimately, stronger business results.”
Beyond Experimental Stages
Investing in agent-enabling AI technology is a proven business collaborative approach that lies in the future of customer service factor, emphasized Bradford. Studies show a direct correlation between AI adoption and improved customer satisfaction, increased agent productivity, and reduced operational costs.
HappyOrNot’s CRM platform is a prime example. By combining real-time customer and employee feedback with AI analysis, businesses can pinpoint areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions that lead to a more positive and productive work environment.
This collaborative approach lies in the future of customer service, and HappyOrNot is at the forefront of this exciting revolution.
HappyOrNot serves 4,000 brands, including health care organizations, Amazon, Google, airports, and retailers across 135 countries. The firm collected and reported on over 1.5 billion feedback responses to provide AI tech that enables other companies to identify and optimize customer and patient experiences through various touchpoints and in-moment feedback data.






















































Social CRM
See all Social CRM